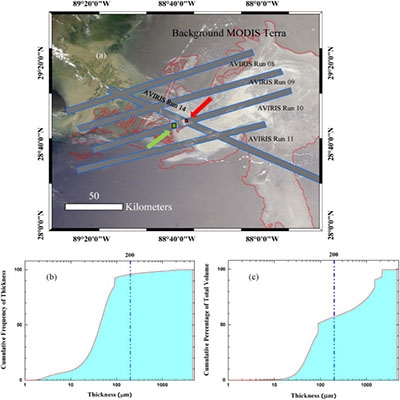
Oil slick morphology derived from AVIRIS measurements of the Deepwater Horizon oil spill: Implications for spatial resolution requirements of remote sensors
Using fine spatial resolution (~ 7.6 m) hyperspectral AVIRIS data collected over the Deepwater Horizon oil spill in the Gulf of Mexico, we statistically estimated slick lengths, widths and length/width ratios to characterize oil slick morphology for different thickness classes. For all AVIRIS-detected oil slicks (N = 52,100 continuous features) binned into four thickness classes (≤ 50 μm but thicker than sheen, 50–200 μm, 200–1000 μm, and > 1000 μm), the median lengths, widths, and length/width ratios of these classes ranged between 22 and 38 m, 7–11 m, and 2.5–3.3, respectively. The AVIRIS data were further aggregated to 30-m (Landsat resolution) and 300-m (MERIS resolution) spatial bins to determine the fractional oil coverage in each bin. Overall, if 50% fractional pixel coverage were to be required to detect oil with thickness greater than sheen for most oil containing pixels, a 30-m resolution sensor would be needed.